According to this belief, when a person breaks a mirror—whether by accident or carelessness—it disrupts their spiritual balance, resulting in seven years of misfortune. This superstition stems from the idea that mirrors reflect not only physical appearance but also the soul. It is believed that damaging a mirror damages one’s soul, which then takes seven years—the length of time ancient Romans thought it took for the body to renew itself—to heal. To avoid the curse or lessen its effect, various remedies have been suggested, including burying the broken mirror shards under moonlight or pulverizing them completely to prevent one’s reflection from being trapped. Practitioners might also avoid looking into a cracked mirror believing residual misfortune remains embedded in it.
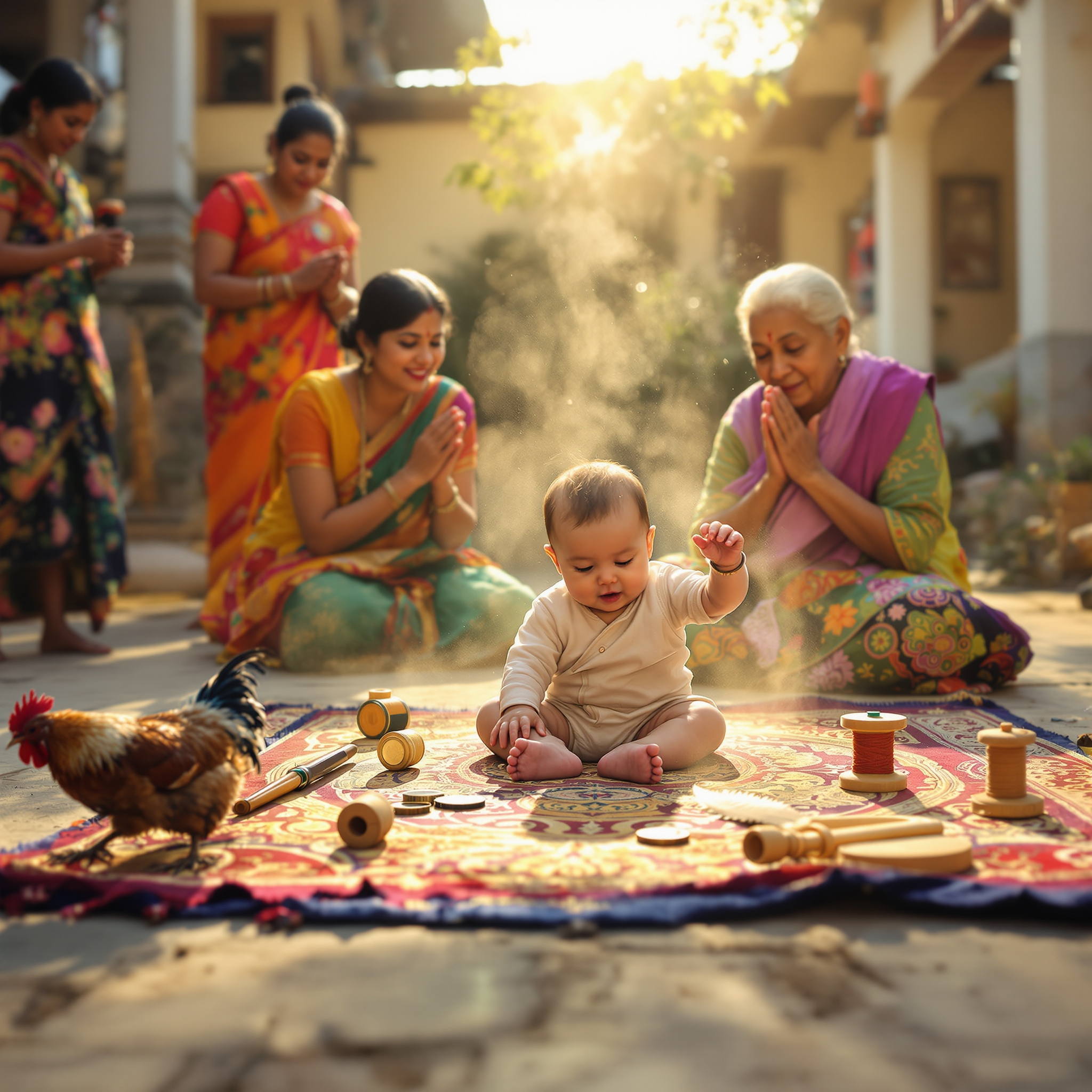

A baby’s future career or fate is predicted by the first object they select during a ceremonial setup.
In several Asian and Eastern European cultures, a traditional ceremony is held for babies usually around their first birthday. Known