According to widespread folk belief across multiple cultures, a dog’s extended, mournful howling during nighttime hours—particularly when unprovoked and directed toward a specific house—warns of approaching death for someone in that household. This canine prediction supposedly reflects dogs’ ability to perceive supernatural entities or sense impending death before humans can. Some traditions specify that the warning intensifies if multiple dogs join the howling, if it occurs during specific moon phases, or if the dog displays additional unusual behaviors like digging or refusing to enter certain rooms.
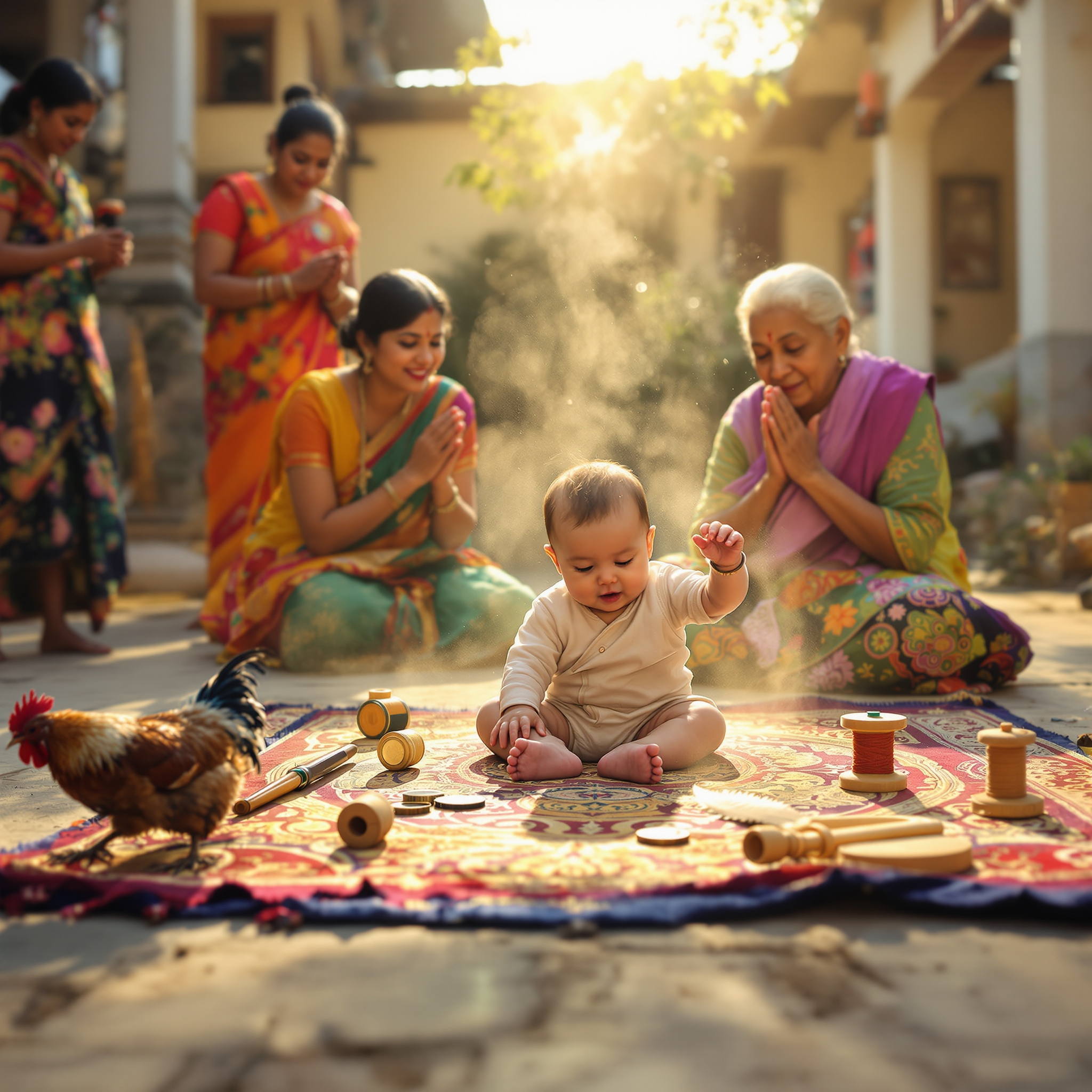

A baby’s future career or fate is predicted by the first object they select during a ceremonial setup.
In several Asian and Eastern European cultures, a traditional ceremony is held for babies usually around their first birthday. Known